Closure of right costophrenic sinus without parenchymal infiltration in... Download Scientific
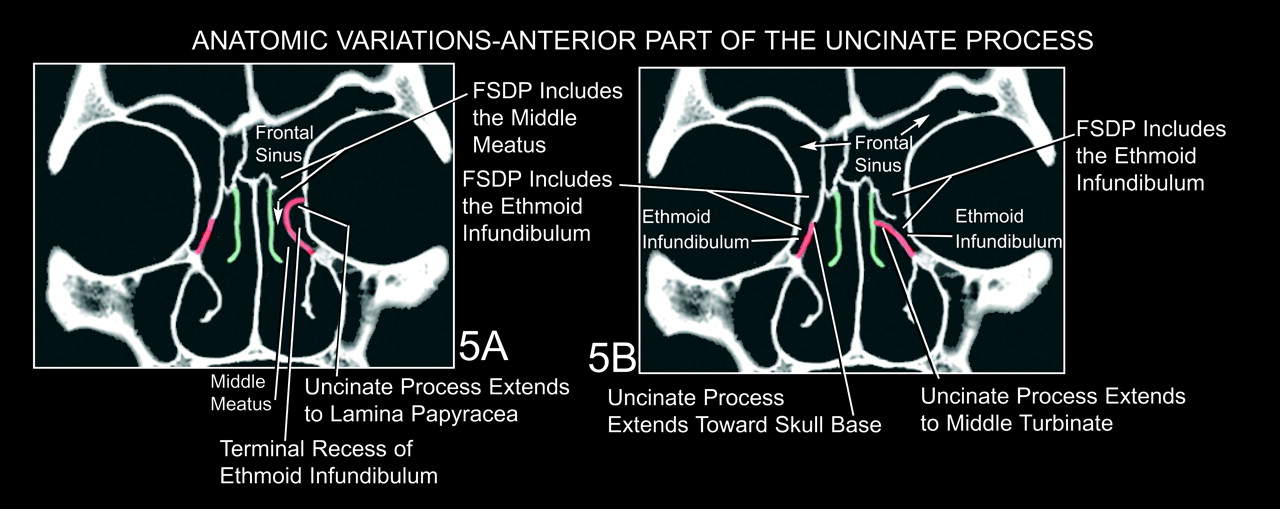
Fig 5. The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures American Journal of
Common symptoms of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps include: Runny, stuffy nose. Mucus running down the throat, also known as postnasal drip. Not being able to smell. Not being able to taste. Facial pain or headache. Pain in the teeth. A sense of pressure over the forehead and face. Snoring.

FileBilateral Cleft Lip With Nasal Deformity.jpg Embryology
09:29. permisi dok, saya mohon penjelasan pada hasil foto thorax saya tertulis asimetris, kurang inspirasi. sinus phrenicocostalis kanan terpotong, kiri tajam. mohon penjelasan dari hasil tersebut dok apakah ada kelainan karena di bagian itu saya kurang paham. jika ada kelainan bagaimana penanganannya. terima kasih.
Costophrenic Angles Chest XRay MedSchool
The study, which looked at 157 sinus dilations, including 98 of the maxillary sinuses, found that for 92% of the patients, the Sinus and Nasal Quality of Life Survey score showed moderate to large improvement. The study's subjects were aged 2 to 21 years, with 30 of the 50 patients undergoing procedures performed concomitantly with dilation.

CT scan image montrant les fractures du sinus maxillaire bilatéral Photo Stock Alamy
Terimakasih atas pertanyaannya. Sinus kostrofrenikus adalah sudut yang dibentuk antara diafragma dan tulang rusuk (iga). Dalam kondisi normal, sudut sinus kostofrenikus pada pemeriksaan radiologis memang akan tampak lancip (tajam), karena tidak terdapat cairan di daerah tersebut. Karenanya, pernyataan yang Anda sebutkan mengindikasikan suatu.

Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling using desmopressin or corticotropicreleasing hormone
The nasal cavity is a roughly cylindrical, midline airway passage that extends from the nasal ala anteriorly to the choana posteriorly.[1] It is divided in the midline by the nasal septum. On each side, it is flanked by the maxillary sinuses and roofed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses in an anterior to posterior fashion.[1] While seemingly simple, sinonasal anatomy is composed of.

Bilateral Inferior Petrosal Sinus Sampling
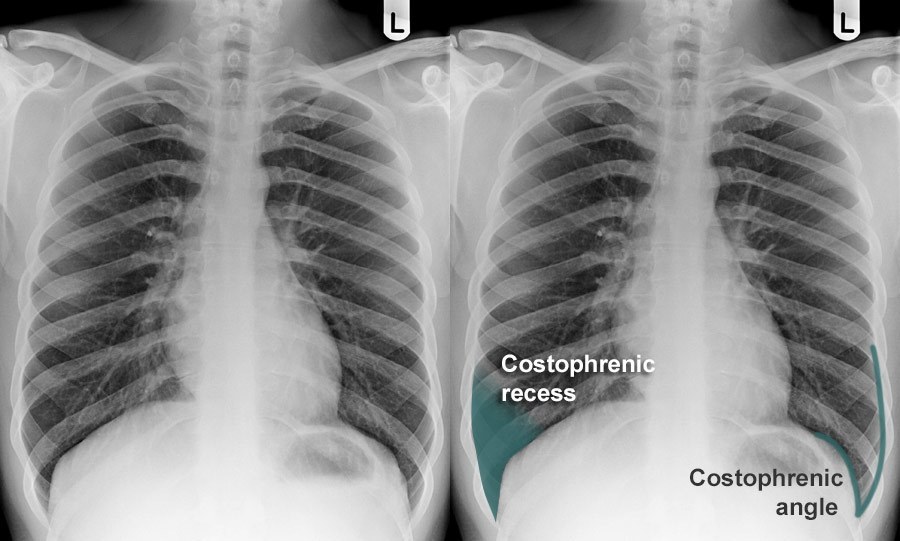
Key points. Pleural effusions are not the only cause of blunt costophrenic angles. Blunting of the costophrenic angles is usually caused by a pleural effusion, as already discussed. Other causes of costophrenic angle blunting include lung disease in the region of the costophrenic angle, and lung hyperexpansion.

Closure of right costophrenic sinus without parenchymal infiltration in... Download Scientific
Detecting effects of antibiotic treatment on the sinus microbiome is challenging. It is likely that potential effects are - like the sinus microbiota in general - highly individual (Liu et al., 2013; Wagner Mackenzie et al., 2019b), rather than manifesting as clear patterns across entire cohorts. The analysis tools that are presently used.
Chest Xray Anatomy Costophrenic recesses and angles
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) may be broadly defined as an inflammatory disorder of the paranasal sinuses and linings of the nasal passages that lasts 12 weeks or longer. More precisely, it is a heterogeneous group of related disorders that share certain clinical and pathologic features. In the past, CRS lacked a clear definition and was.

Nasal endoscopy revealing bilateral nasal polypoid lesions in the... Download Scientific Diagram
The development of bilateral sinuses was firstly evaluated, including unilateral hypoplasia with contralateral dominance or bilateral balanced development. A hypoplastic sinus was defined as a sinus that is 40% smaller in average caliber than the contralateral sinus which could be called "dominant" . Then, 4 types of anatomic variations.

[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Sphenoid Sinuses
The costophrenic angle, also known as the diaphragmatic angle, is an essential anatomical structure observed in medical imaging, particularly chest X-rays and CT scans. This angle is formed at the junction of the chest wall (the ribs) and the diaphragm, which is the muscular partition that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity.
PPT RADIOLOGI BLOK KDS I PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5430666
Sinonasal polyposis pattern. polypoid masses in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. bilateral maxillary infundibulum widening. convex ethmoid air cell walls. attenuation (change) the nasal septum and ethmoid air cell walls. +/- infundibular, ostiomeatal, sphenoethmoidal recess patterns depending on secondary obstruction.
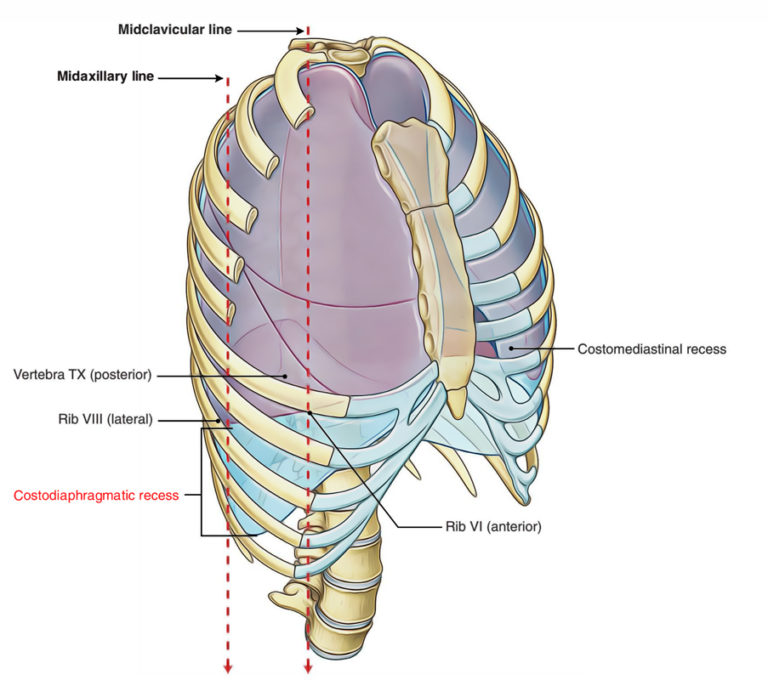
Costodiaphragmatic Recess Earth's Lab
Symptoms. Common symptoms of chronic sinusitis include: Thick, discolored mucus from the nose, known as a runny nose. Mucus down the back of the throat, known as postnasal drip. Blocked or stuffy nose, known as congestion. This makes it hard to breathe through the nose.

Fibrous pericardium = Pericardial sinuses YouTube
Choanal polyp. A choanal polyp is a benign solitary sinonasal mass that originates in a paranasal sinus and secondarily extends into the nasal cavity. The most common type is the antrochoanal polyp, which originates in the mucosa of the maxillary sinus or antrum. The polyp opacifies and slightly enlarges the sinus cavity with no bone destruction.

PPT RADIOLOGI BLOK KDS I PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5430666
Vina, terima kasih telah berkonsultasi dengan kami di Alodokter.com. Berdasarkan dari bacaan foto Rongten Thorax yg anda sampaikan tersebut ada 2 item yg menunjukkan adanya abnormal atau tidak normal yg sedang terjadi pada paru-paru suami anda, yaitu : Adanya infiltrat minimal paracardial bilateral. corakan bronchovaskular sedikit meningkat.

Sinus Kostofrenikus Dan Diafragma Kanan Berselubung
Costodiaphragmatic recess. The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, [1] is the posterolateral fringe of the pleural space, a potential space around the lung inside the pleural cavity. It is located at the acutely angled junction ("reflection") between the costal and diaphragmatic parietal.

Sinuses X Ray Positioning
Methods: Cases of isolated sphenoid sinus lesions encountered in the neurosurgical setting which had rare pathologies are discussed. Pathologies such as Langerhans cell histiocytosis, solitary plasmacytoma, chordoma, pituitary adenoma, leiomyosarcoma, fungal infection, and mucocele which appeared primarily in sphenoid sinus are discussed along.