Atomic structure and properties. (Chapter 3) презентация онлайн
Atomic structure and properties. (Chapter 3) презентация онлайн
The Shape of d Orbitals Solved Example Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs Orbitals Chemistry There are four different kinds of orbitals, denoted s, p, d and f each with a different shape. Of the four, s and p orbitals are considered because these orbitals are the most common in organic and biological chemistry.

FileD orbitals.svg Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
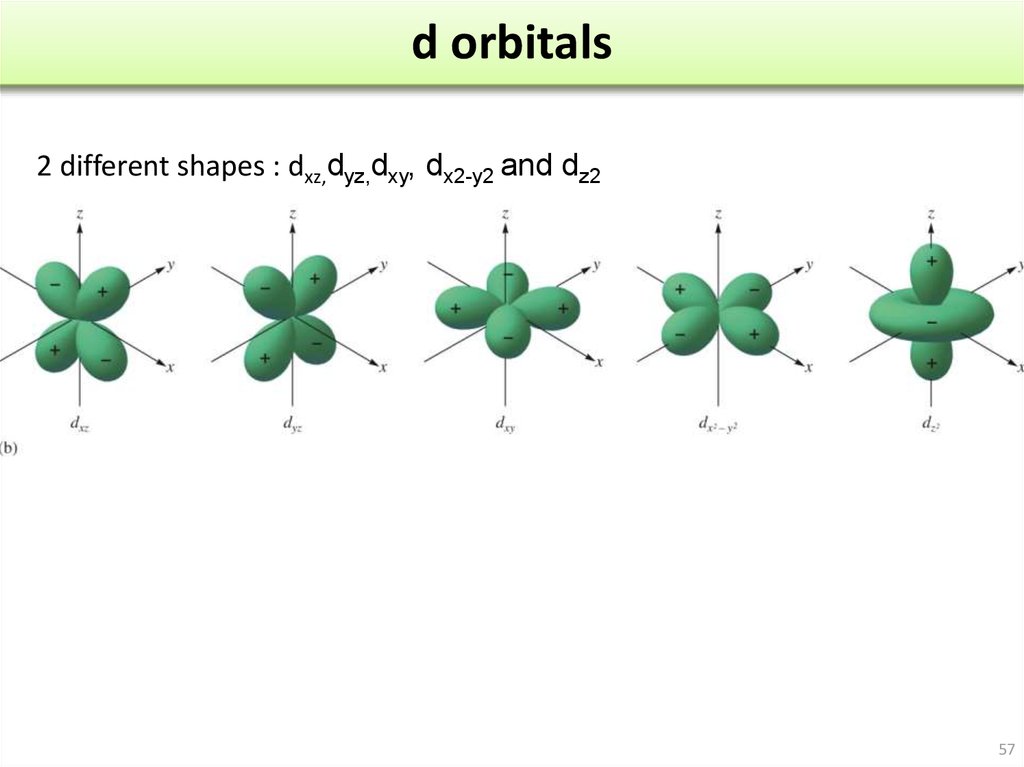
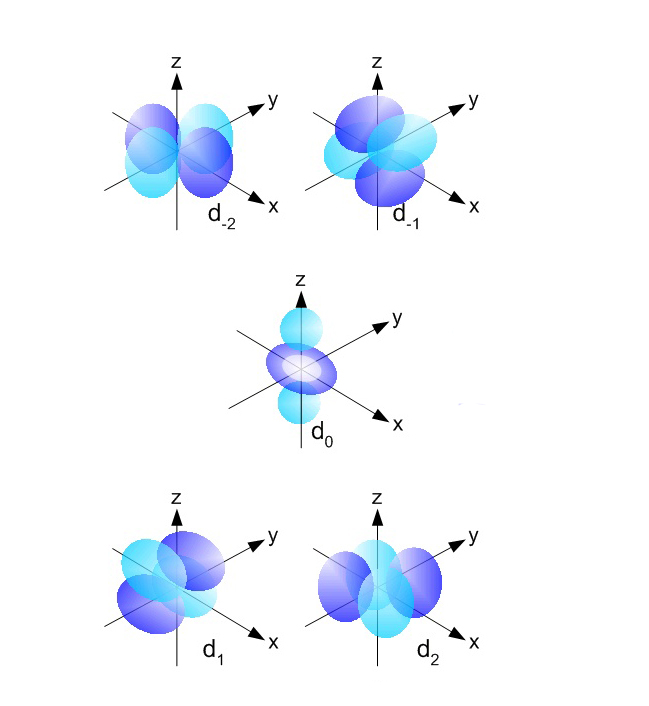
There are a total of five d orbitals and each orbital can hold two electrons. The transition metal series is defined by the progressive filling of the 3d orbitals.These five orbitals have the following ml values: ml=0, ±1, ±2, Explore other atomic orbitals s-orbitals | 2p-orbitals | 3p-orbitals | 3d-orbitals | 4f-orbitals

Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Shape of s, p, d, f Orbitals, FAQs, Examples
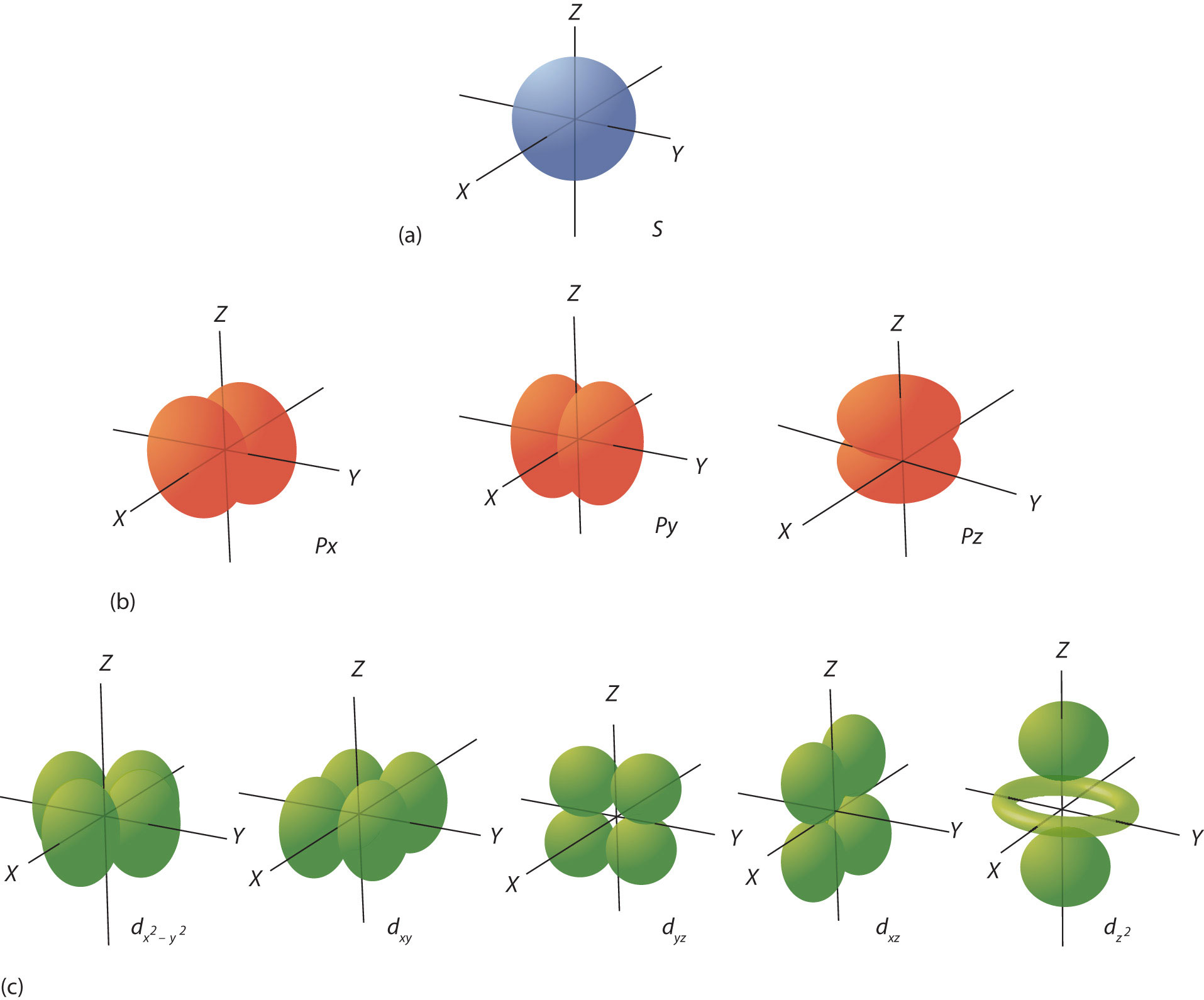
The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in each case, like a hollow ball made of rather chunky material with the.

Atom Electrons, Orbitals, Energy Britannica
As the world's leading provider of launch services - and the only provider with an orbital class reusable rocket - SpaceX has deep experience with both spacecraft and on-orbit operations. Learn More. 30 DAY TRIAL. If not satisfied, return Starlink for a full refund. Service Address.

Chemical bonding Atomic Orbitals, Shapes, Hybridization Britannica
Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The number "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The letter "s" indicates the shape of the orbital: s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus— they look like hollow balls made of chunky material with the nucleus at the center.

Atomic Orbitals D
the spacecraft orbital inclination d. Assessment of spacecraft compliance with Requirement 4.7-1 ODAR Section 8: Assessment for Special Classes of Space Missions Specify the special mission class(es) and detail how the ODAR addresses additional measures applied to the mission. The following is an example for tether systems: a.

À quoi correspondent les orbitales électronique ? Et les nombres quantiques ? CouleurScience
configuration species excited states d^0 Ca+2, Ti+4, Sc+3 0 d^1 Ti+3 1 d^2 V+3 3 d^3 Cr+3 3 d^4 Mn+3 1^*d^5 Mn+2, Fe+3 0 d^6 Fe+2 1^*d^7 Co+2 3 d^8 Ni+2 3 d^9 Cu+2 1 d^{10} Zn+2 0^* *Jahn-Teller distortion breaks the expected degeneracy. See also: Electron Orbital , Transition Element . Quantum Chemistry: Orbitals: d-Orbitals : configuration:
Atomic Theory IV Chemistry Visionlearning
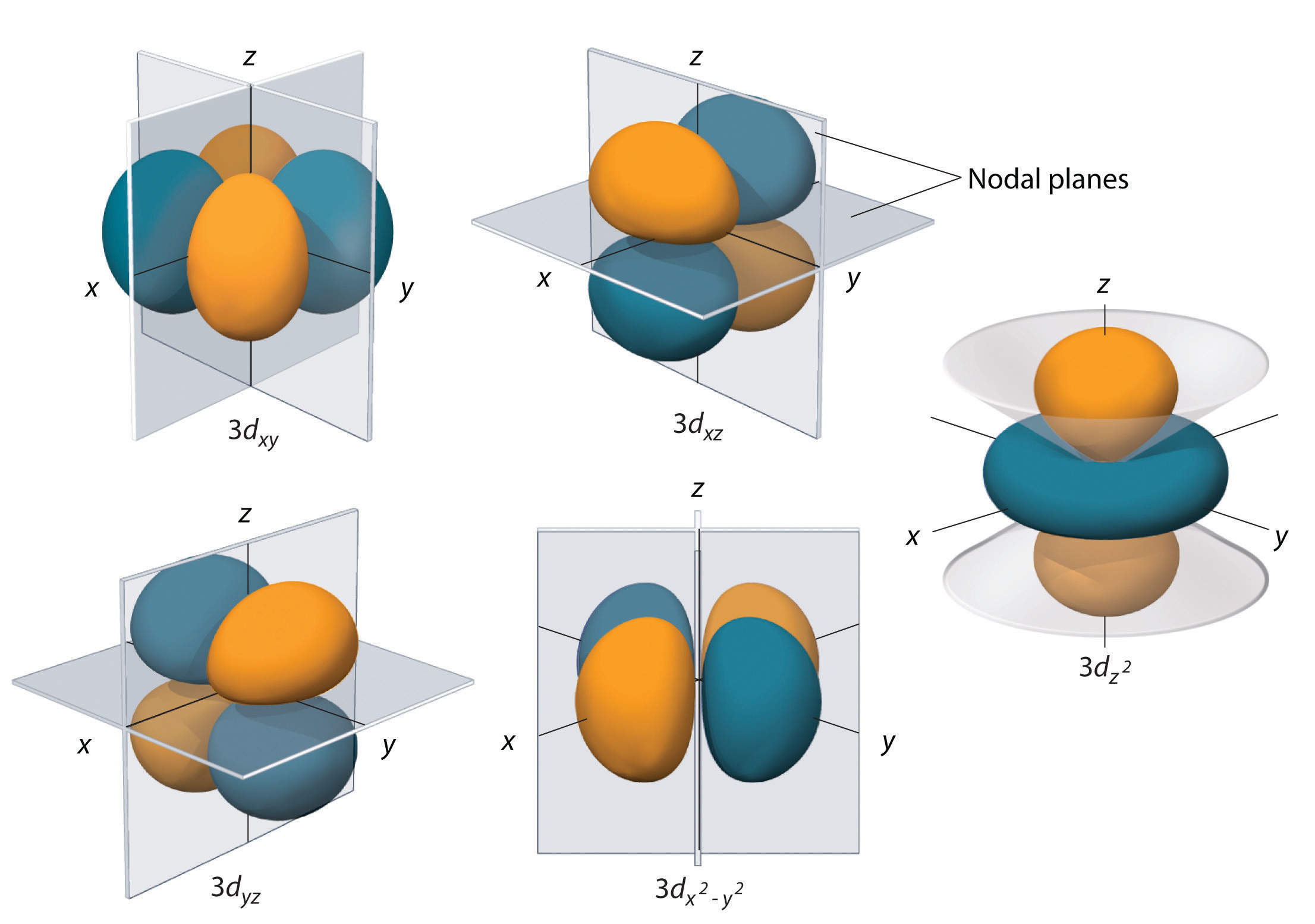
Generally, there are three types of bonding and antibonding interactions that may occur with d d orbitals: sigma ( σ σ ), pi ( π π ), and delta ( δ δ) bonds. Figure 5.1.3.1 5.1.3. 1: The five 3d 3 d orbitals are shown. The orientation of the axes is consistent and the z z axis is horizontal for convenience in drawing bonding along the z z.
3.7 Electron Arrangement The Quantum Model Chemistry LibreTexts
Mechanistic insights into electrocatalytically reduced OER performance in marigold-like trimetallic NiFe-based LDH: Charge localisation and d-band orbital filling S. Deka, M. K. Jaiswal, P. Rajput and B. Choudhury, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D3TA07489G
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
An orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of Bohr's orbit. In contrast to his concept of a simple circular orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron.
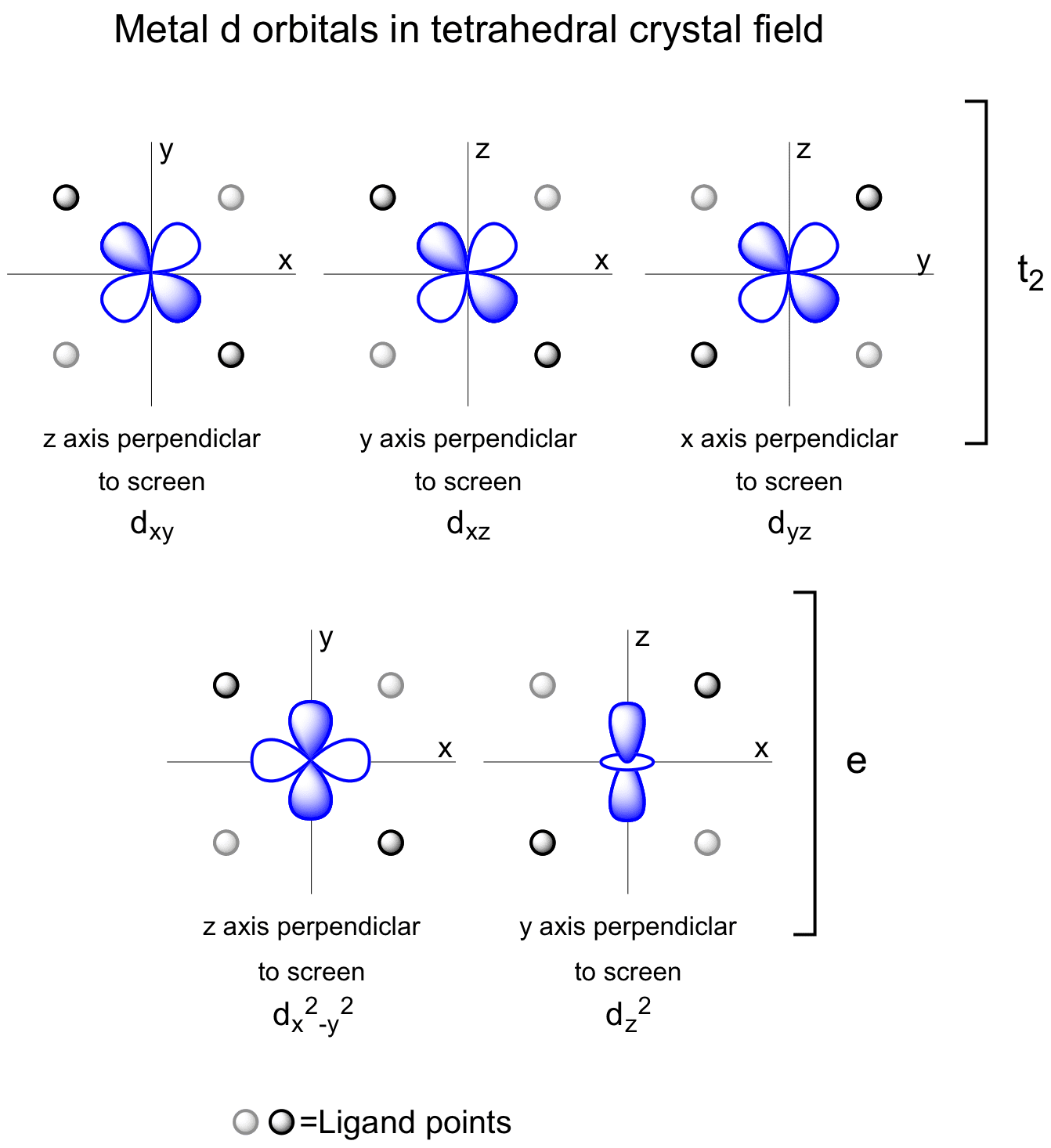
Metal d orbitals in a tetrahedral crystal field
The d-orbitals are even less well known than the s and p-orbitals which preceded them. Since they are inti-mately involved in transition metal chemistry, chemists must understand them reasonably well. We deal with them here, starting with the d z2 orbital, and then con-sidering the d xy orbital and the d x 2−y orbital. III. d z2 ORBITALS

Atomic Orbitals D
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital ( / ˈɔːrbɪtəl /) is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. [1] This function describes the electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a specific region around the nucleus. [2]
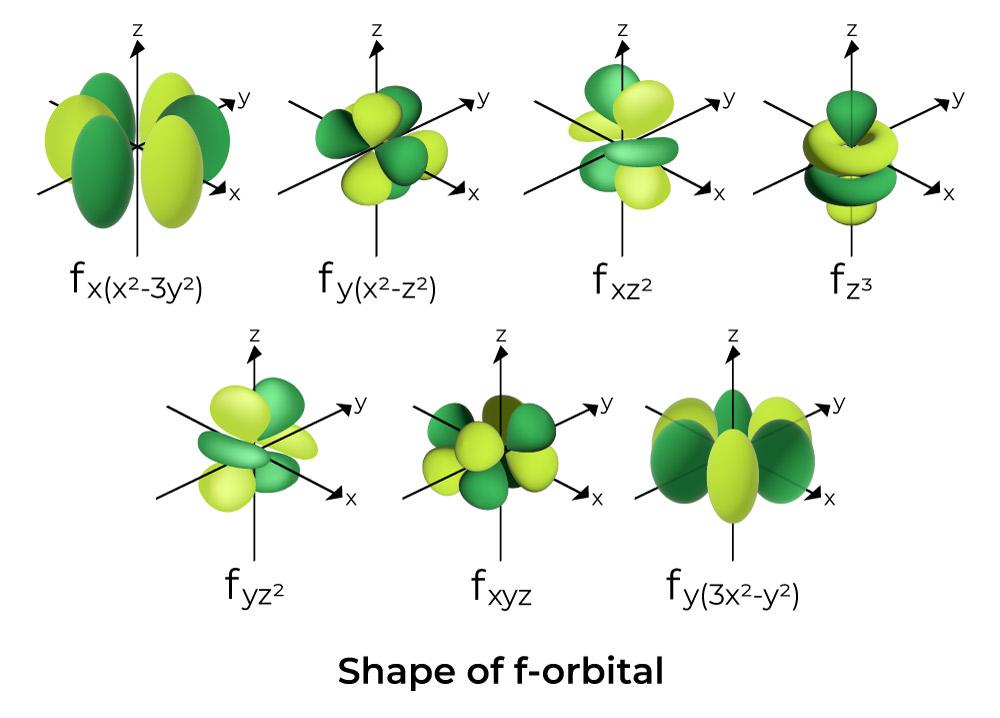
D Orbitals Signs
A fourth d orbital has lobes lying along the x and y axes; this is the \(3d_{x^2−y^2}\) orbital. The fifth 3d orbital, called the \(3d_{z^2}\) orbital, has a unique shape: it looks like a \(2p_z\) orbital combined with an additional doughnut of electron probability lying in the xy plane. Despite its peculiar shape, the \(3d_{z^2}\) orbital is.
Atomic Orbitals D
orbital, in chemistry and physics, a mathematical expression, called a wave function, that describes properties characteristic of no more than two electrons in the vicinity of an atomic nucleus or of a system of nuclei as in a molecule. An orbital often is depicted as a three-dimensional region within which there is a 95 percent probability of.
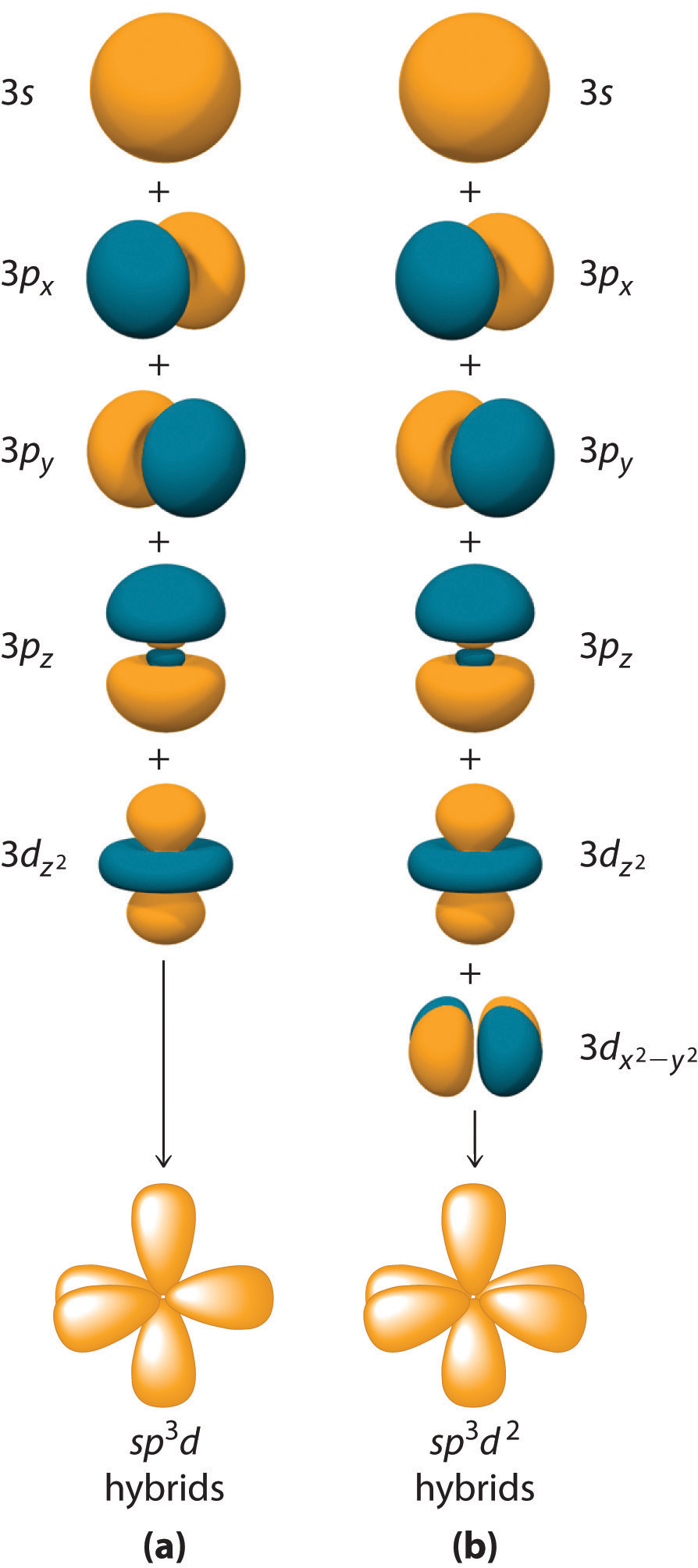
Localized Bonding and Hybrid Atomic Orbitals
Electronic Structure of Atoms s, p, d, f Atomic Orbitals In today's post, we will talk about the atomic orbitals. So, first, what is an orbital? In a formal, quantum mechanical definition, orbitals are essentially probability distribution maps for electrons within atoms.
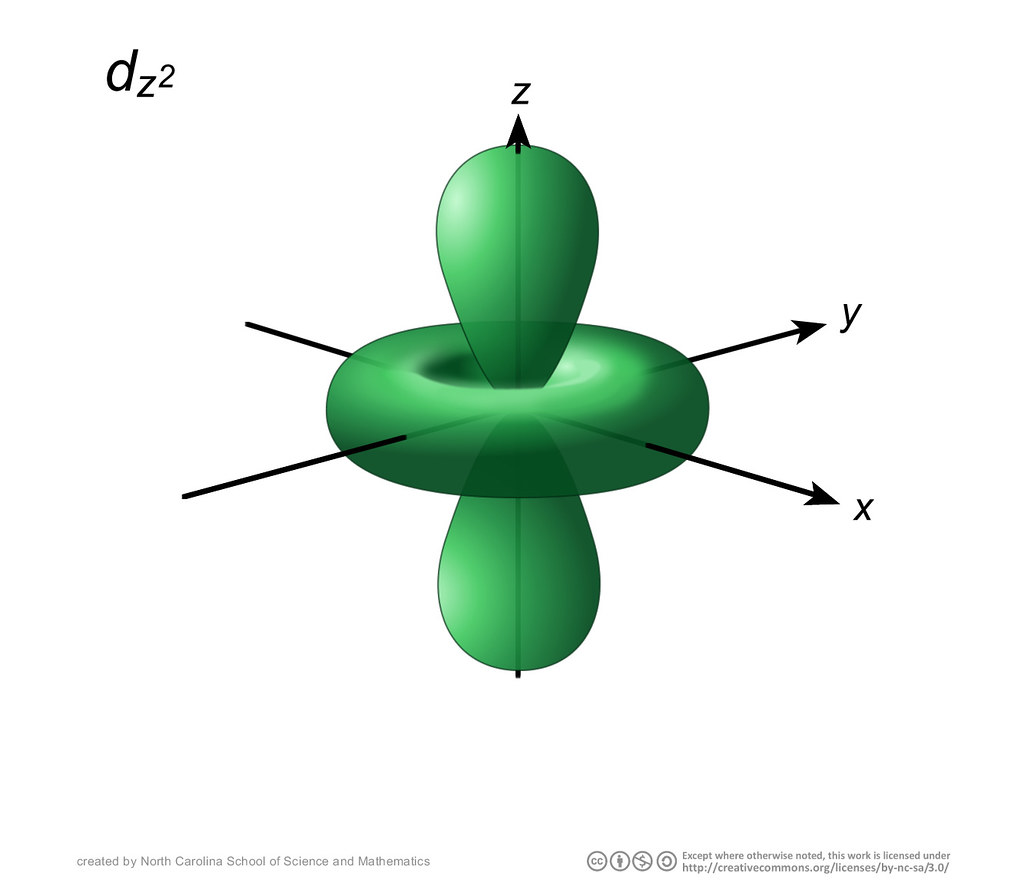
dorbital_dz2.jpg NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in … Flickr
digedag 10 years ago An orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. We classified the different Orbital into shells and sub shells to distinguish them more easily. This is also due to the history when they were discovered. Start with the easy. Imagine shells around the nucleus, that get bigger and bigger.